Is Eth Crypto A Good Investment Summarized Insights
When pondering the question is eth crypto a good investment, one must delve into the intricacies of Ethereum's blockchain technology and its applications. Understanding Ethereum goes beyond just its comparison with Bitcoin; it involves exploring its diverse use cases across various industries that showcase its potential.
Market trends play a crucial role in assessing Ethereum’s value, particularly as its historical price movements and trading volume reveal much about its volatility and market capitalization. Moreover, investors must weigh the risks and regulatory environment surrounding Ethereum, which can significantly impact their investment decisions.
Understanding Ethereum
Ethereum, launched in 2015, is a decentralized platform that enables developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It operates on a blockchain, similar to Bitcoin, but with its unique features that allow for more complex functionalities. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily serves as a digital currency, Ethereum's primary purpose is to serve as a platform for dApps and smart contracts, which automatically execute agreements when certain conditions are met.While Bitcoin is often viewed as a store of value or "digital gold," Ethereum is more of a versatile tool for developers.
Its programmable nature allows for an array of use cases across various industries. For instance, Ethereum is utilized in finance (DeFi), supply chain management, gaming, and even in digital art through non-fungible tokens (NFTs). This versatility makes Ethereum a strong contender in the cryptocurrency space.
Market Trends for Ethereum

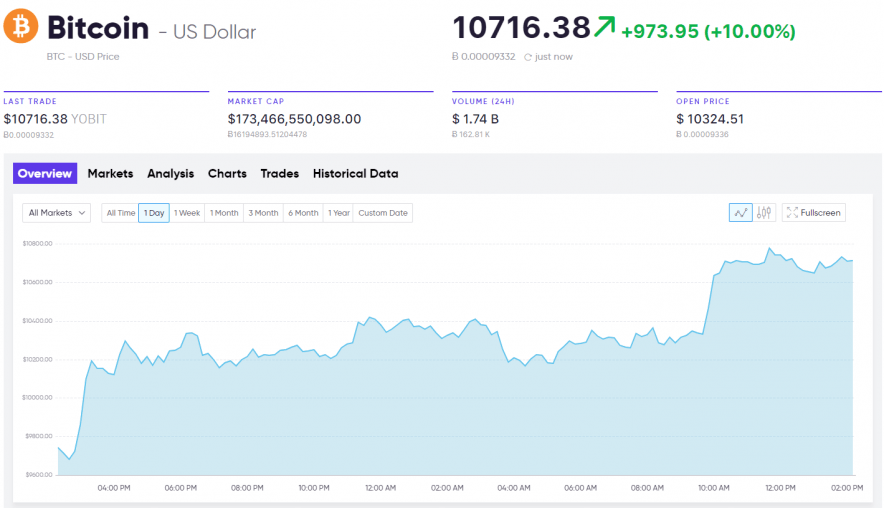
Currently, Ethereum is experiencing significant market trends that impact its value. Over the past year, Ethereum has shown considerable growth, influenced by increasing adoption and advancements in technology. With Ethereum 2.0's transition to proof-of-stake, many investors are optimistic about its potential for scalability and sustainability.Historically, Ethereum's price movements have been volatile, with notable peaks and troughs. For instance, in 2021, Ethereum reached an all-time high of over $4,800, reflecting a surge in interest and investment.
Its market capitalization consistently ranks second after Bitcoin, showcasing its dominance in the crypto market. Trading volume has also increased, indicating active participation from both retail and institutional investors.
Investment Risks and Considerations

Investing in Ethereum does come with several risks that potential investors should consider. The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and Ethereum is no exception. Sudden price fluctuations can result in significant gains or losses, making it crucial for investors to be aware of their risk tolerance.Additionally, the regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrencies is still evolving. Governments worldwide are developing frameworks to regulate crypto assets, and any changes in regulations can significantly impact Ethereum's price and legality.
Investors must stay informed about these developments to make educated decisions.Common pitfalls include over-investing based on hype and failing to conduct thorough research. Many new investors are drawn to the market due to potential high returns but often lack a solid understanding of the underlying technology and market dynamics.
Comparisons with Other Cryptocurrencies
When comparing Ethereum's performance with other major cryptocurrencies, it becomes evident that Ethereum offers unique advantages. For instance, while Bitcoin is focused on being a digital currency, Ethereum's capability to support smart contracts and dApps sets it apart. This versatility can provide more opportunities for growth in various sectors.Compared to altcoins, Ethereum has established itself as a leader due to its extensive developer community and a robust ecosystem.
In the table below, we compare Ethereum with other popular cryptocurrencies to illustrate its unique features.
| Cryptocurrency | Launch Year | Main Purpose | Consensus Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | 2015 | Smart contracts, dApps | Proof-of-Stake (Ethereum 2.0) |
| Bitcoin | 2009 | Digital currency | Proof-of-Work |
| Cardano | 2017 | Smart contracts, dApps | Proof-of-Stake |
Future Predictions for Ethereum

Experts are optimistic about Ethereum's future, especially with the ongoing developments in its technology. The transition to Ethereum 2.0, which aims to enhance scalability and reduce energy consumption, is a significant milestone that could positively impact its value. Predictions suggest that as more developers adopt the platform for various applications, Ethereum's utility and demand will continue to grow.Upcoming technological advancements, such as sharding and improvements to the protocol, are expected to further bolster Ethereum's position in the market.
Major events on the Ethereum roadmap, including the full implementation of Ethereum 2.0, are highly anticipated by investors and could signal a new era of growth for the platform.
Portfolio Diversification Strategies
Including Ethereum in an investment portfolio can enhance diversification. Investors should consider strategies that balance their exposure to crypto assets by allocating a portion of their portfolio to Ethereum while maintaining investments in traditional assets like stocks and bonds. A common approach is a balanced asset allocation model where investors might hold 5-10% of their portfolio in Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies.Diversification is crucial in cryptocurrency investments due to the market's inherent volatility.
By spreading their investments across different assets, investors can mitigate risks and potentially capitalize on Ethereum's growth while protecting against downturns in other areas.
Resources and Tools for Investors
For those looking to invest in Ethereum, several reputable platforms facilitate trading. Popular exchanges like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken offer user-friendly interfaces and robust security measures for buying and selling Ethereum.Tracking Ethereum's price and market performance can be accomplished through various tools and websites, such as CoinMarketCap and CoinGecko, which provide real-time data and analytics.Moreover, engaging with communities and forums like Reddit or Discord can offer valuable insights and discussions among Ethereum investors, enhancing understanding and investment strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, while Ethereum presents exciting investment opportunities due to its technological advancements and market trends, it's essential to approach it with caution. By diversifying portfolios and staying informed about future predictions, investors can make more informed choices when considering whether Ethereum is the right fit for their investment strategy.
Helpful Answers
What are the main advantages of investing in Ethereum?
Investing in Ethereum offers potential for high returns due to its innovative technology, active development community, and various use cases.
How does Ethereum’s volatility compare to Bitcoin?
Ethereum tends to exhibit higher volatility than Bitcoin, which can lead to both significant gains and losses for investors.
What should investors be wary of when investing in Ethereum?
Investors should be cautious of market speculation, regulatory changes, and the potential for technological vulnerabilities.
Are there reputable platforms for trading Ethereum?
Yes, platforms like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken are widely regarded as reputable options for trading Ethereum.
How can one track Ethereum’s market performance effectively?
Investors can use tools like CoinMarketCap or CoinGecko to monitor Ethereum's price, market cap, and trading volume in real-time.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1020578114-ef76f9318757449fa0d5fdcf955d93af.jpg)